-
 What is a Domain Name and Web Hosting: Complete Analysis and Tips for Affiliates03.11.2022Reading Time: 12 minutes
What is a Domain Name and Web Hosting: Complete Analysis and Tips for Affiliates03.11.2022Reading Time: 12 minutesIn the previous article about API, we discussed how to add a landing page to a hosting and how to pick up your domain name for it. But before you start running traffic via API and designing your website, you need to create a correct domain name and move it on a safe hosting.

Today, we’ll learn what domain and hosting are, and also tell you why every affiliate needs to know this.
Let’s go!
What is a domain name
There are two roles: a user who wants to find your website on the Internet. The user types the name of your site in the search bar and gets to the main page of it, which will be displayed as direct traffic (direct) in analytics services. And here is you, the website creator, who has everything to launch this site on the Net: a server that stores all the resource files, and an easy-to-remember name, known as a domain name. The second is what allows users to access your website through the browser address or search bars, while DNS does all the hard work.
Consider the example of AdCombo. If we type a combination – adcombo.com – in the address or search bars in the browser:
we get to the main page of the AdCombo website with the same name:
People often confuse the terms of “website” and “domain”, but there is a huge difference between them. A website is a web page that is displayed on the Internet, in other words, content. And the domain name of the site is its unique name, the “address” where users will find and see its content.
Types of domains
To create a website, you need to register a domain name first . Domains consist of levels. There are three levels of domains – the first (top), second and third levels.
Top-Level Domains are also called domain zones. These are domains tied to a territory or theme of the site. They are not for sale, as they are owned by a specialized organization – ICANN, and are distributed among certain areas where we can register the site.
They are also divided into subgroups:
- Domain zones indicate countries – National Domains (ccTLD – country code Top-Level Domain), for example:
.ca – Canada;
.de – Germany;
.au – Australia.
- They indicate the type of organization using the domain name – International (general) Domains (gTLD – generic Top-Level Domain), for example:
.com is for commercial organizations.
.info – information sites.
.edu – educational resources.
- Or they indicate the theme of the site – New International Domains (new gTLDs), for example: .photography, .business, .fitness, etc.
Second-Level Domains are registered at theTop-Level Domains.
They are separated from the domain zone by a dot and often used for websites and for commercial purposes, so you can create your own domain name and or buy an existing one.
A requirement of registering such a domain name is its uniqueness, so it won’t work to buy another domain name with an already existing one.
An interesting fact: the most expensive domain name deal was made in 2005. The lasvegas.com domain name was sold for $90 million.
Here is an example of Second-Level domain: adcombo.com, google.com, etc.
The Third-Level is a resource within the Second-Level Domain. The examples of the Third-Level Domains are adventure.adcombo.com and blog.adcombo.com.
Typically, the Third-Level is used when creating a web resource on a site builder or hosting individual sites inside a large web portal – for example, forum.example.com.
So the domain name structure looks like this:

There may be a WWW (World Wide Web) prefix also known as subdomain in the address bar of any site, before the main domain name, for example:

The WWW prefix means an information system that provides access to textual information via the http or https protocol.
Many years ago, when the Internet was quite young, and servers were low-powered, the prefix was used to separate servers within a network. One of the articles says that every company ran its network of servers, and each server within the network was considered a hosting that performed only one role. Depending on the role, the hosting provided, it would get a specific hostname:
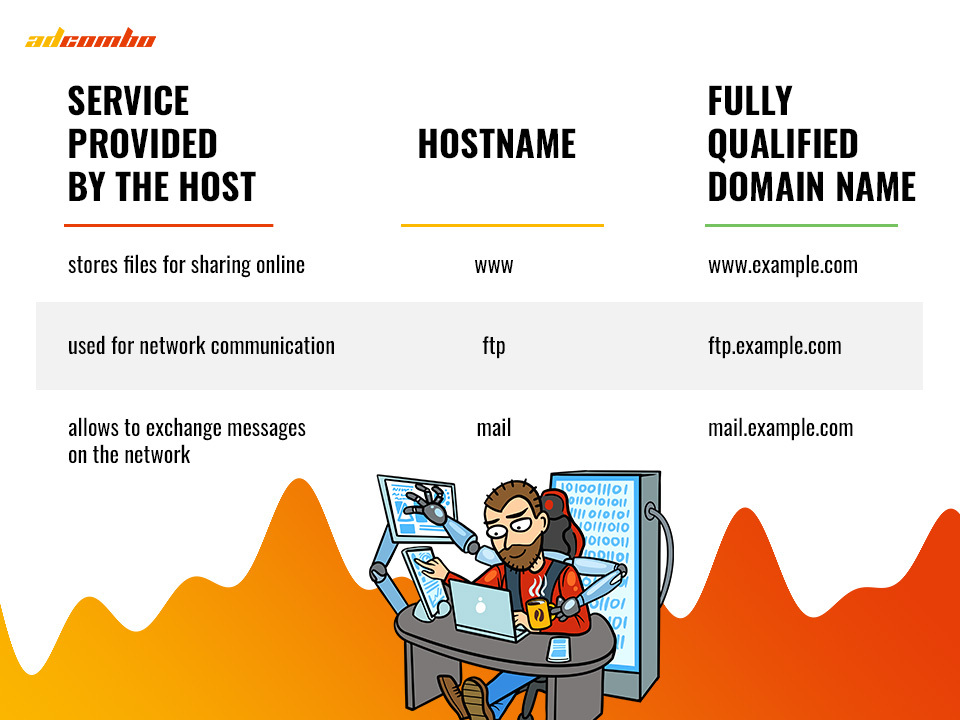
Nowadays, WWW is considered a remnant, since there is no need for the prefix. However, it’s still found on many sites, and many users continue to use it in search queries.
Thus, the site promotion becomes more difficult, since many search engines mark the domain.com and www.example.com as different sites (domains of different levels).
This means that all external links are divided into two parts, depending on how they were placed – with or without WWW. If a site owner loses some external links to the site, this may lead to a downgrade, and less users will visit it.
Usually, in order to avoid such problems, they set up a 301 redirect from a non-canonical site (let’s say, www.example.com) to a canonical/preferred site (example.com). Therefore, users who enter www.example.com/page07 will see example.com/page07 in the address bar of the browser. You can read more about this in the article.
How to create a domain name
Now let’s briefly go over the steps that need to be done to a domain name. First of all, there are two ways to make a domain: create it on a domain registrars website or get it fromyour web hosting provider (we’ll talk about it further). If you choose the first option, then follow the steps:
- Choose a domain zone
Here you need to know the reason and purpose of your future domain name. If you want to run business in a certain country, then register a national domain name, and if you provide some services or launch your own project, then look at thematic names.
- Let’s think of a name
Take the issue seriously, because it directly impacts website promotion and passing moderation. The ideal choice for a site name is one with the main keyword and relevant to the advertised product.
Lifehack # 1: as we mentioned earlier, you can create your own domain name even if there is no website. This is beneficial because search engines better index resources that have been registered for a long time, therefore, the promotion will bring results faster.
- Select the registrar and check the name for uniqueness
This can be done on the registrar’s website or through the whois service. In this article, we will not consider each of the services in detail. We’ll name examples of the top registrars according to Forbes, so you can take a closer look at them and take for the use:
- namecheap.com – has a low extension cost for top-level domains.
- domain.com – suitable for short-term projects.
- domains.google – fine for those who have already chosen hosting.
Lifehack #2: Taking foreign domains on foreign sites is better. If the name is occupied, but you really like it, just change its registration zone.
- Setting up a domain
After checking the domain name for uniqueness and compliance with the requirements of the selected zone, you get access to your domain name. Usually, account settings come after payment is made.
Lifehack #3: the domain must be registered to the name and email you specified. If another owner is indicated – you’d better choose another registrar.
- Upload the site to the hosting
If you have already created a site before registering a domain, then transfer the files to the newly bought domain − read the instructions. If necessary, add a database or fill out the one that was created automatically for your new hosting.

What is a DNS Server
So, you have created the website domain. Now the question arises: “How can a user quickly find exactly your site out of 1000 similar ones?”.
In the same manner as telephone numbers, domain names are also organized in a global network of servers – the Domain Name System (DNS). This system sends the user directly to your site and provides quick access to it.
To connect to a server with a specific site, you need to know its IP address (Internet Protocol) – a unique address that identifies a device on the Internet or local network. Using long combinations of numbers is inconvenient, so IP addresses are associated with text names – domains. For example, adcombo.com is easier to remember than a set of numbers, right?
What happens from the user side: the system uses the IP address as an identifier to find the specific site to which access is requested. Then it converts the IP address into a format that the user can understand – a domain name.
Thus, DNS servers store information about domains, make it available to users at their request, and also cache DNS records of other servers.
You don’t have to have a separate DNS server because it is included in your hosting provider’s services. What to do if the domain registrar and hosting are different services, we will tell you below.
Now, we’re moving on to hosting.What is Web Hosting
Note that domain and web hosting are basic services for creating a website on the Internet. The domain is the address of the site, while the hosting is the space where it’s actually located.
Let’s imagine that you want to create your own landing page for selling Titan Gel. Any site consists of a set of files (texts, graphic materials, program scripts, database, etc.), that are not enough to store only on a computer. If you want to make customers see the precious landing pages and increase not only their poten…tial but also your sales, the content should be online as well.
The hosting comes to the rescue, when you need a space to place your landing page for profit (as you’re lucky enough).
Hosting features include:
- Providing access to a domain
As mentioned above, hosting allows a user not only to register a domain name, but also to manage it;
- Providing access to the server
Hosting “maintains” a site and prepares it for users to respond quickly to requests while involving minimal effort and spend of its owner;
- Providing storage space
To place multimedia content (images, audio, and video) on the page, a user requires a significant amount of disk space. Therefore, it is easier to store such data on a server, which the user will always have access to through a hosting provider. And some of them even provide a backup service in case of unexpected troubles with the site.
How to choose the right web hosting
First, let’s define the selection criteria:
- Website loading speed is important for ranking;
- Continuity of work (uptime). Optimal – is 99.9%, in extreme cases – is 98.9%;
- Security tools – built-in antiviruses, SSL, backups;
- The type of hosting must match the features of the resource to be hosted.
Then, you need to decide why you need this hosting at all. Web hostings can be divided into the following types:
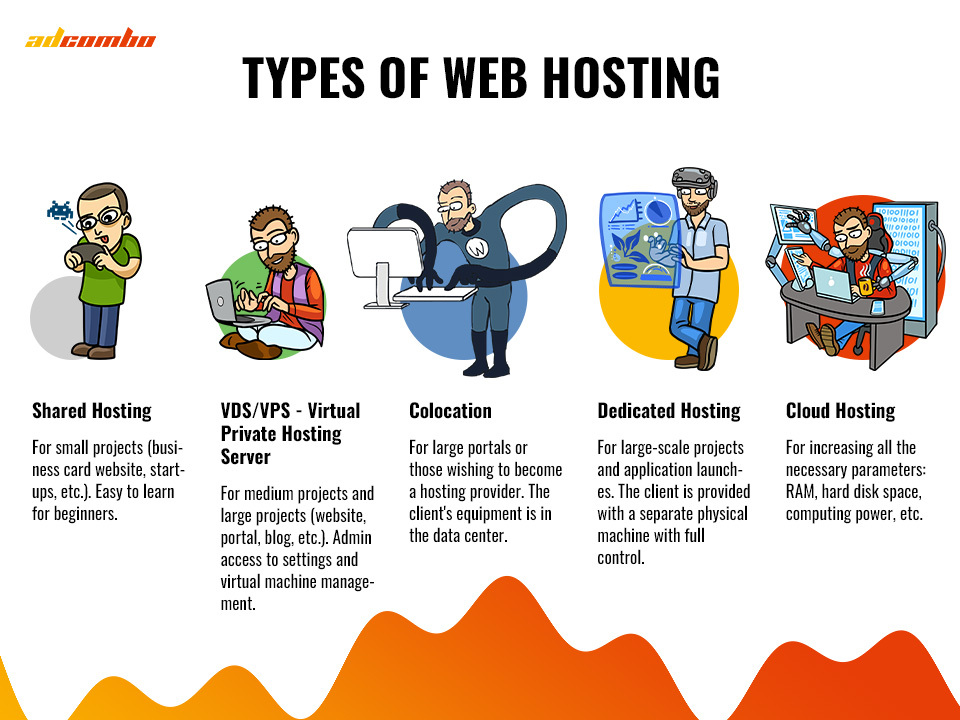
- Shared Hosting
The most common type of hosting suitable for small projects.
Its advantages:- cheap ($2–15 per month);
- convenient for the average user who needs a control panel (with a minimum number of settings) to upload files, create site backups, etc.;
- easy to use even for inexperienced users (the general server configuration is handled by the hosting provider).
This type of hosting provides a rather limited amount of space on the hard disk of a remote server. It’s also the most vulnerable to viruses and doesn’t support stable work of a site.
If you haven’t tried your hand at being a system administrator, you can use this hosting for practice, but for more complex projects and stable work, we advise you to take a closer look at the other types.
- VDS or VPS – Virtual Private Hosting Server
It’s suitable for medium and big projects, and involves the allocation of a part of the remote server for a separate virtual machine for each client (up to 20 within the server). The advantages are:
- independence from other server clients;
- separate OS on each virtual machine;
- ensuring the stable functioning of the site due to the guaranteed values of computing power, the amount of RAM, etc.;
- admin access to settings and management of a dedicated virtual machine;
- self-installation of preferred software.
The complexity of installing and configuring software on a VDS server requires having sysadmin skills. Another disadvantage is also the direct proximity to other virtual machines, which jeopardizes the security of the site. But this type of web hosting is much safer than shared hosting.
- Colocation
It differs from VDS in that the hosting provider is cheaper and only provides a specialized space in its data center for installing your personal equipment and a dedicated channel for Internet access.
Besides, it:- has connection to communication channels with high bandwidth;
- is suitable for large projects;
- is suitable for those who want to become a hosting provider.
- Dedicated Hosting
Suitable for large-scale Internet projects. You will have access to a separate remote server with a high level of security and full control, while as a hosting company it only monitors the state of the hardware.
If you are already an experienced system administrator ready for complex installation/management and paying a high price ($100-500 per month), then you can surely choose this server type.
- Cloud Hosting
Due to the additional power of the cloud, you can increase all the necessary parameters: RAM, hard disk space, computing power, etc. Depending on how much resources are used, this hosting service varies in price.
A universal option for maintaining the site without obvious flaws.
How to connect a domain to web hosting
So, if you have registered a new domain and want to link it to existing hosting, then just change the domain settings in your personal account. Follow two steps:
- Find out the NS-servers of your hosting
Where: find it in the hosting control panel, in a letter from the provider, or ask support. There must be at least two of these addresses: one primary and one additional;
- Specify NS-servers in domain settings
Where: in your personal account, find the item with the purchased domains -> DNS and specify the hosting NS-servers there.
Lifehack #4: if you need to transfer your domain from one hosting to another, change the domain settings by specifying the NS-servers of the new hosting there.
How to create a trusted domain
If you have read the article up to this point and discovered something new for yourself – this means now you have one more affiliate skill. In this paragraph, we will combine all the above recommendations and give a couple of new tips to make your site convert.
- You should not save on the domain zone. Better use a Top-Level Domain zone (like .com, .net, .org) like most big companies do. This will increase the credibility for moderators and reduce the risk for the ad campaign to be banned at the very start;
Lifehack #5: You can buy old domains with a history, which also increases trust.
- Try to choose a domain name in accordance with the theme of the site / product being advertised. State its purpose or use the main keyword so that it becomes clear for users where are they going and why;
- Even if you don’t use the WWW prefix, set up a 301 redirect. This will allow you not to miss traffic to your site. Also, you will need the redirect when transferring the site to another domain name or web hosting, as well as to quickly switch from tablets and mobile devices to a version of the site adapted for them;
- Be sure to include the Privacy Policy on the website. It can be generated, edited and embedded to the site in less than 10 minutes. This significantly reduces the risks of a ban;
- Before launching an advertising campaign, get a security certificate − SSL (Secure Sockets Layer). It protects the data that users leave on the site. This is a must-have part for sites that are engaged in online sales and want to reach the top of the search queries list. Otherwise, the ad campaigns will be banned, and the site won’t lift to the top;

If you see a padlock icon − “secure connection” next to the domain name, then the site seems more trustworthy, and, therefore, the time of interaction with it may increase. You can complete this point in the following way:
- Get a free SSL certificate for moderation with basic data encryption features. Remember that the level of protection of such certificates is lower than that of paid ones;
Popular services are Let’s Encrypt, GoDaddy, SSL For Free. Other options can be found in the article;
- Provide certification to such paid providers with favorable conditions, such as SSL.com, Comodo and others;
- Park your domain in AdCombo, read this article to learn how to do it;
- When choosing a DNS service, prioritize fast query response, uptime, and high quality of service;
- Choose a hosting based on your needs, the project scale and your experience. If you don’t have a system administrator experience, then pick a shared virtual hosting. It’s quite suitable for uploading a landing page to your own domain. If you want to make your changes to the landing page, install self-hosted trackers to make the best version out of it. Think about more expensive and reliable providers, for example, VPS/VDS servers.

Great job! Today we have learned what domain name and web hosting are, and also found out why it is impossible to succeed in affiliate marketing without them.
We hope that this article will be useful in getting your sites ready for work and will also encourage you to gain IT knowledge. The more an affiliate marketers know, the better their profits are.There are more educational articles ahead, but for now, you can reward our labor with likes and subscriptions in our social networks.
Wish you trusted domains, converting sites and super profits!
- Domain zones indicate countries – National Domains (ccTLD – country code Top-Level Domain), for example:




Stunning Website, I hadn’t noticed blog.adcombo.com before my searches!
Carry on the vast on!